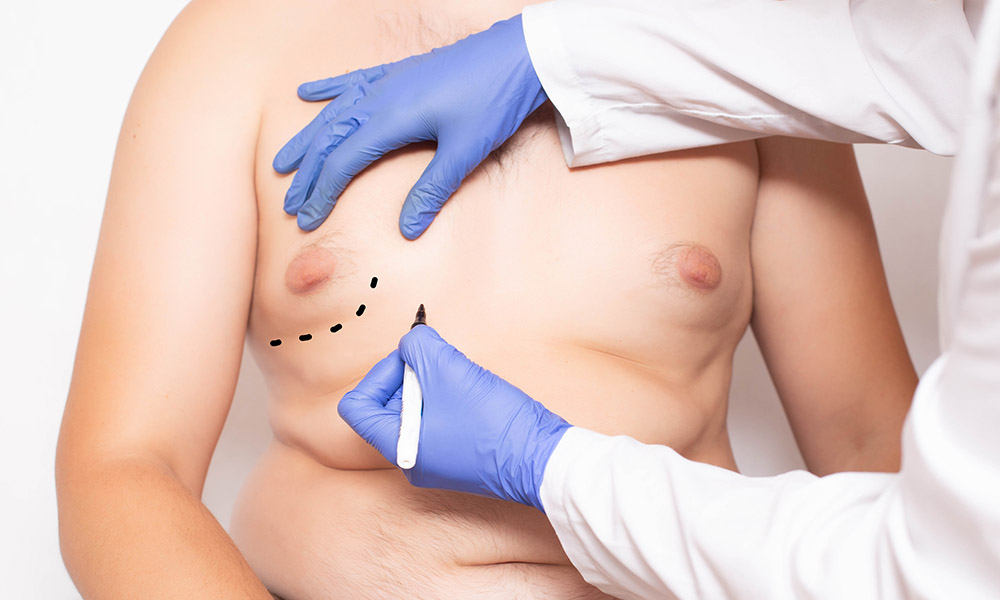
Gynecomastia is the abnormal growth of breast tissue in men. It can impact one or both breasts and is mostly caused by an imbalance between the hormones, estrogen and testosterone. When estrogen levels increase or testosterone levels drop, breast tissue may start to grow. This condition is different from regular fat buildup that comes from weight gain because it involves the growth of glandular tissue, not just fat. Gynecomastia can appear at any age but is most common in newborns, teenagers, and older men.
In newborns, temporary breast swelling happens due to maternal hormones and usually disappears within a few weeks. During puberty, many boys develop mild breast enlargement, which often goes away naturally as hormones balance out. Whether someone is considering Gynaecomastia Surgery in Mumbai seeking general information, in older men, the condition can occur because testosterone levels decrease with age while estrogen levels rise.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia can result from many factors that disturb hormone balance. It may occur naturally during puberty or ageing, but can also be triggered by medical issues or certain medications. Conditions such as liver disease, kidney problems, thyroid disorders, or hormone-secreting tumours can all contribute.
Stages of Gynecomastia
Grade I – Early Stage
In the first stage, symptoms are mild. The person may feel tenderness or soreness around the nipples. A small lump of firm tissue might form under the nipple, which can be felt when touched. The breast area may look slightly swollen, but there is no extra skin growth.
Grade II – Moderate Stage
In this stage, the breast tissue grows more and becomes visibly larger. The nipples may appear more prominent, and the area beneath them feels firmer. There can be mild asymmetry, where one breast is slightly larger than the other. The skin might stretch a bit, and some men may feel uncomfortable wearing tight clothing.
Grade III – Advanced Stage
At this stage, the enlargement becomes more obvious. The breasts contain a mix of glandular and fatty tissue, causing them to look fuller and more prominent. Some extra skin growth may also occur. The condition might cause emotional discomfort and affect self-confidence. In some cases, medicines that regulate hormone levels can help, but surgery may be considered for a more permanent solution.
Grade IV – Severe Stage
This is the most advanced stage of gynecomastia. The breasts become large and droopy, closely resembling female breasts. There is excess glandular tissue, fat, and skin. This can lead to physical discomfort, pain, and difficulty performing activities. It can also cause psychological distress, making the person feel embarrassed or insecure. Surgery is usually the only effective treatment at this stage.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Doctors diagnose gynecomastia through physical examination, imaging tests like ultrasound, and blood tests to check hormone levels. Treatment depends on the cause and stage. For mild cases, monitoring and lifestyle changes may help. If a hormonal imbalance is the reason, medicines can be prescribed. In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove excess tissue and restore a natural chest shape.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, exercising regularly, and avoiding substances that affect hormones can also help manage or prevent gynecomastia.