Key Takeaways:
- The surgical retractor has evolved over time, with advancements in materials and engineering improving their precision and versatility.
- Adjustable blade designs, ergonomic handles, and compatibility with other surgical instruments have been significant innovations in surgical retractors.
- Choosing the right surgical retractor depends on factors such as the type of surgery, patient anatomy, and desired level of tissue exposure.
- Proper sterilization and handling techniques are essential for safety and efficiency in using surgical retractors.
- Retractors can enhance surgical precision through techniques like countertraction and the use of angled retractors.
- Advancements in retractors include robotic-assisted retractors, retractor-assisted tissue regeneration, and their role in advanced imaging techniques.
1. The Evolution of Surgical Retractors
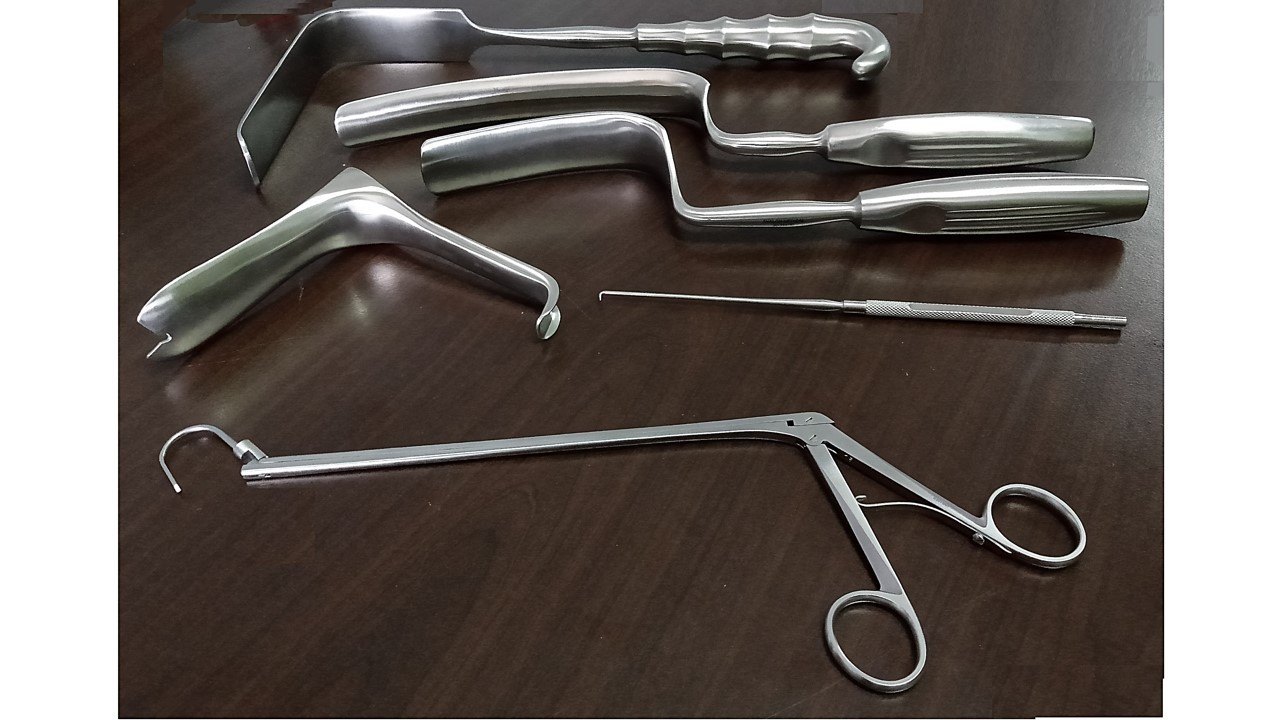
The surgical retractor is a tool that has become an essential part of modern surgery. However, the journey of the surgical retractor began long ago, with primitive tools used by ancient civilizations. These early retractors were simple handheld instruments used to hold back tissues during surgeries, and they lacked the precision and sophistication of modern retractors.
It was not until the 18th century that significant advancements were made in surgical retractors. These revolutionary innovations were driven by the need to improve surgical outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. One such innovation was the introduction of self-retaining retractors, which allowed surgeons to free up their hands and focus on the surgical procedure.
Over time, the field of science began to shape the design and functionality of surgical retractors. The use of materials like stainless steel and titanium made retractors more durable and resistant to corrosion. Additionally, advancements in engineering led to the development of retractors with adjustable blades and various sizes, further enhancing their versatility in different surgical procedures.
The Early Days: From Primitive Tools to Modern Marvels
In the early days of surgery, retractors were basic handheld instruments made from materials such as wood or bone. These crude instruments were used to lift and hold back tissues during surgical procedures. While they served their purpose, they lacked the precision and stability required for complex surgeries.
As surgical techniques became more advanced, the need for better retractors became apparent. Innovations such as the introduction of the self-retaining retractor in the 18th century allowed surgeons to achieve better visibility and access to the surgical site. These retractors had adjustable blades that could be positioned and locked in place, freeing up the surgeon’s hands and improving surgical precision.
In the early 20th century, the development of stainless steel retractors revolutionized the field of surgery. Stainless steel retractors were not only durable but also resistant to corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan and reducing the risk of contamination. This breakthrough allowed surgeons to perform more complex and lengthy procedures without the need for frequent retractor replacements.
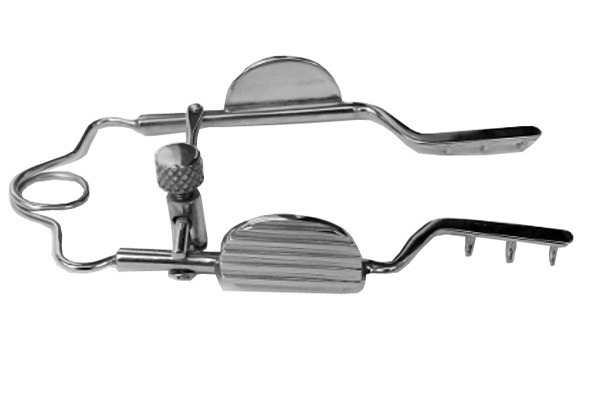

Revolutionary Innovations: How Science Shaped the Surgical Retractor
The field of science has played a vital role in shaping the design and functionality of surgical retractors. Advances in materials science and engineering have led to the development of retractors with improved durability, adjustability, and ergonomics.
One of the most significant advancements in surgical retractors is the use of titanium alloys. These alloys offer high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for surgical instruments. Titanium retractors are not only lightweight but also highly resistant to corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan and reducing the risk of contamination.
Another innovation that has greatly improved the functionality of surgical retractors is the introduction of adjustable blade designs. Adjustable blade retractors allow surgeons to customize the retractor’s shape and size to match the specific needs of the surgical procedure. This flexibility enables surgeons to achieve optimal visibility and access to the surgical site, enhancing surgical precision and reducing the risk of complications.
Ergonomics is another area where science has made significant contributions to surgical retractors. The introduction of ergonomic handle designs has improved the comfort and ease of use for surgeons. Ergonomic handles reduce hand fatigue and provide a secure grip, allowing surgeons to maintain precise control over the retractor during lengthy procedures.
Behind the Scenes: Uncovering the Engineering Secrets of Retractor Design
While the functionality and materials used in surgical retractors are critical, the underlying engineering principles are what make them truly effective. Engineers work tirelessly to optimize the design of retractors, taking into account factors such as stability, ease of use, and compatibility with other surgical instruments.
One key aspect of retractor design is the balance between rigidity and flexibility. Retractors need to be rigid enough to provide adequate tissue exposure and maintain the surgical site’s stability. At the same time, they need to be flexible enough to accommodate the natural variations in patient anatomy and surgical access.
The shape and curvature of the retractor blades also play a crucial role in their effectiveness. Engineers carefully design the blades to ensure optimal tissue retraction while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues. Blade designs can vary depending on the specific surgical procedure, with some retractors featuring curved blades for better access to deep surgical sites.
Compatibility with other surgical instruments is another important consideration in retractor design. Engineers work closely with surgeons to develop retractors that can be seamlessly integrated into existing surgical setups. This compatibility ensures smooth and efficient surgical procedures, allowing surgeons to focus on the task at hand without any hindrances.
2. Choosing the Right Surgical Retractor for Every Procedure
When it comes to surgery, choosing the right surgical retractor is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. There are a variety of retractors available, each designed for specific procedures and patient needs. Surgeons must carefully consider factors such as the type of surgery, patient anatomy, and desired level of tissue exposure when selecting a retractor.
A Scalpel for Every Situation: Exploring Different Retractor Types
Surgical retractors come in various types, each designed for specific surgical procedures. One common type is the hand-held retractor, which is manually operated by the surgeon or an assistant. These retractors are versatile and can be used in a wide range of surgical procedures.
Self-retaining retractors are another type commonly used in surgery. These retractors have an adjustable blade design that allows them to be positioned and locked in place, freeing up the surgeon’s hands. Self-retaining retractors are particularly useful in procedures where prolonged tissue retraction is required.
Specialized retractors, such as neurosurgical retractors, are designed for specific procedures. Neurosurgical retractors, for example, are designed to provide access to the brain while minimizing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues. These retractors often feature adjustable blades and specialized handle designs to facilitate delicate procedures.
Customization is Key: Adapting Retractors to Individual Patient Needs
Every patient is unique, and surgeons must take into account factors such as patient anatomy and specific needs when selecting a retractor. Adjustable blade retractors allow surgeons to customize the retractor’s shape and size to match the patient’s anatomy, ensuring optimal tissue retraction and visibility.
In addition to adjustable blades, some retractors feature interchangeable components that allow for further customization. For example, certain retractors have interchangeable blades of varying sizes and shapes, allowing surgeons to adapt the retractor to the specific needs of the procedure and patient.
Size Matters: Selecting the Appropriate Retractor for Optimal Outcomes
The size of the retractor is another critical factor to consider when selecting a surgical retractor. The size should be appropriate for the specific surgical procedure and patient anatomy to ensure optimal tissue exposure and surgical access.
Smaller retractors are often used in procedures where precision and delicacy are essential, such as neurosurgery or ophthalmic surgery. These retractors allow for better visibility and access to intricate anatomical structures without causing unnecessary trauma or damage.
On the other hand, larger retractors may be required for procedures that involve more extensive tissue retraction, such as abdominal or orthopedic surgeries. These retractors provide greater tissue exposure, allowing surgeons to perform the necessary steps of the procedure with ease.
3. Mastering the Art: Best Practices for Surgical Retractor Use
Using surgical retractors effectively requires more than just selecting the right instrument. Surgeons must also master the art of retractor placement, sterilization, and handling techniques to ensure safety, efficiency, and optimal surgical outcomes.
Ensuring Safety and Efficiency: Proper Sterilization and Handling Techniques
Proper sterilization of surgical retractors is critical to prevent the risk of infection and contamination. Retractors should be thoroughly cleaned and sterilized using validated techniques before each use. This includes pre-cleaning to remove any visible debris, followed by sterilization using autoclaving or other approved methods.
Handling retractors with care is also essential to avoid damage and ensure their longevity. Retractors should be handled gently and stored properly when not in use. Proper handling techniques involve avoiding excessive force, keeping retractors away from sharp objects or surfaces, and using protective covers to prevent any potential damage.
Optimizing Visibility: Techniques for Effective Retractor Placement
Proper retractor placement is crucial for achieving optimal visibility and access to the surgical site. Surgeons must carefully position retractors to ensure adequate tissue retraction without causing unnecessary trauma or interference with the surgical field.
One common technique for effective retractor placement is the use of a hand-held retractor in conjunction with a self-retaining retractor. The hand-held retractor can be used initially to lift and hold back tissues, while the self-retaining retractor secures the retraction once the desired exposure is achieved.
The use of surgical assistants can also greatly facilitate effective retractor placement. Assistants can help the surgeon position and stabilize the retractors, allowing the surgeon to concentrate on the surgical procedure without worrying about retractor manipulation.
Mind over Matter: Enhancing Surgical Precision with Retractor Utilization
Retractors not only provide access and visibility but also play a crucial role in enhancing surgical precision. Surgeons must develop a deep understanding of retractor utilization techniques to make the most out of these tools.
One important technique is the concept of countertraction. Countertraction involves applying opposing forces to tissues surrounding the surgical site. By doing so, surgeons can create a tension-free operating field, making it easier to perform delicate maneuvers and achieve precise surgical outcomes.
Another technique that can enhance surgical precision is the use of angled retractors. Angled retractors can provide unique access to anatomical structures that may be difficult to visualize using straight retractors alone. Surgeons can manipulate these angled retractors to achieve optimal exposure and improve their surgical precision.
4. Advancing Surgical Techniques: Cutting-Edge Applications of Retractor Technology
The field of surgery is constantly evolving, and surgical retractors are no exception. From robotic-assisted retractors to retractor-assisted tissue regeneration, innovative advancements are pushing the boundaries of surgical techniques and improving patient outcomes.
Pioneering Precision: Robotic-Assisted Retractors in Minimally Invasive Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery has revolutionized the field of minimally invasive surgery, and retractors play a crucial role in these advanced procedures. Robotic-assisted retractors are equipped with robotic arms and specialized control systems that allow surgeons to perform complex maneuvers with enhanced precision and control.
These retractors can be manipulated using robotic interfaces, reducing the need for direct manual manipulation by the surgeon. Robotic-assisted retractors can provide more stable retraction and better visualization, leading to improved surgical outcomes, reduced intraoperative complications, and faster recovery times for patients.
Unlocking New Possibilities: Retractor-Assisted Tissue Regeneration and Repair
Retractors are not only used for tissue retraction but can also play a vital role in tissue regeneration and repair. Retractor-assisted tissue regeneration techniques aim to harness the body’s natural healing processes to promote tissue regrowth and repair.
By strategically placing retractors, surgeons can create controlled tension or compression on tissues, stimulating the regeneration of new blood vessels, collagen deposition, and tissue remodeling. These techniques have shown promising results in various surgical specialties, including plastic surgery and orthopedic surgery.
Next-Level Visualization: The Role of Retractors in Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging techniques, such as intraoperative imaging and fluorescence-guided surgery, are becoming increasingly important in modern surgical practice. Retractors play a crucial role in these techniques by providing optimal tissue exposure for imaging and visualization.
Specific retractors have been designed to work in conjunction with imaging devices, allowing surgeons to achieve the best possible visualization during surgery. These retractors may have features such as integrated light sources, fiber-optic cables, or specialized attachments for imaging probes.
By combining retractors with advanced imaging techniques, surgeons can accurately visualize anatomical structures, identify tumor margins, and make more informed decisions during surgery, ultimately improving patient outcomes.