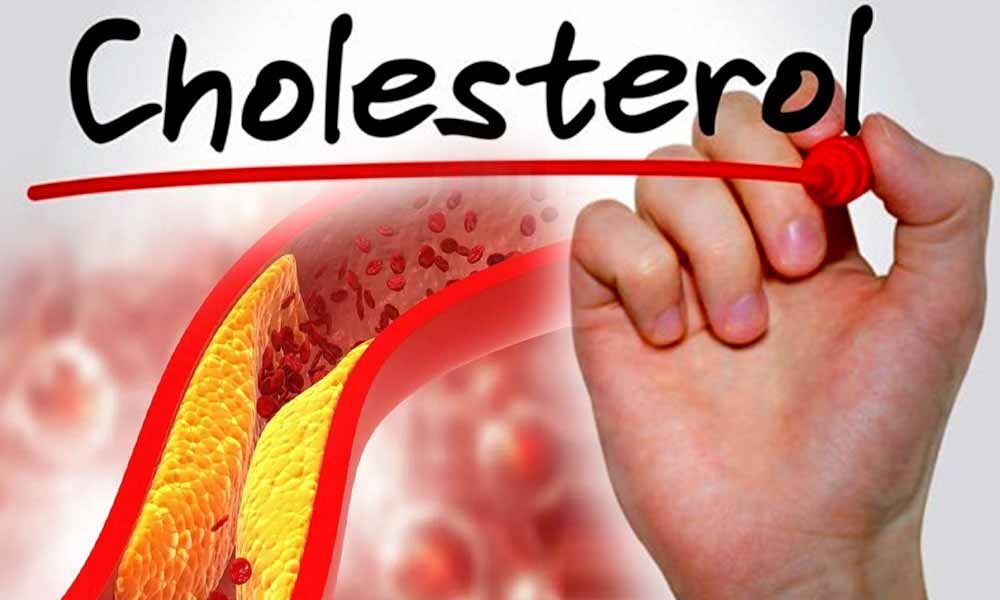
Cholesterol is often associated with negative health outcomes, particularly in relation to cardiovascular disease. However, cholesterol also plays an important role in brain health and function.
What is Cholesterol?
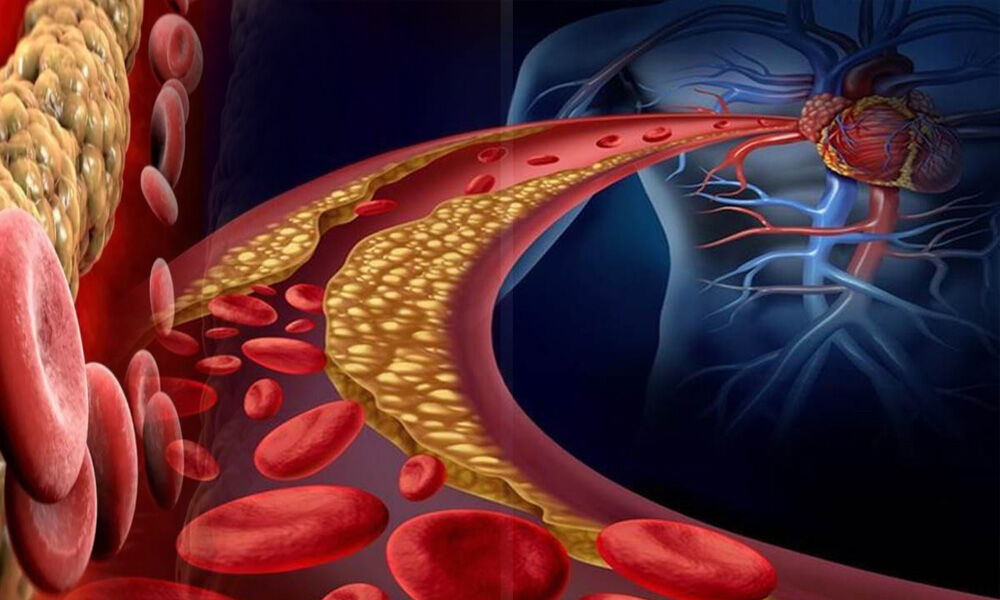
Cholesterol is a type of fat that is produced by the liver and is found in certain foods. It is essential for the production of cell membranes, hormones, and vitamin D. There are two types of cholesterol: high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
HDL, also known as “good” cholesterol, helps to remove excess cholesterol from the body. LDL, or “bad” cholesterol, can build up in the walls of arteries and increase the risk of heart disease.
The Brain and Cholesterol
The brain is made up of millions of nerve cells, or neurons, that communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. These signals are transmitted across synapses, which are the tiny gaps between neurons.
Cholesterol plays an important role in the formation and function of synapses. It helps to maintain the structural integrity of synapses and promotes the release and uptake of neurotransmitters, which are the chemical messengers that allow neurons to communicate.
In addition, cholesterol is involved in the production of myelin, which is the fatty substance that surrounds and insulates nerve fibers. Myelin helps to speed up the transmission of signals between neurons, which is essential for normal brain function.
The Benefits of Cholesterol for Brain Health
Research has shown that maintaining healthy levels of cholesterol may have a number of benefits for brain health. For example:
- Cholesterol has been linked to improved memory and cognitive function in older adults.
- Low levels of cholesterol have been associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
- Cholesterol may protect against the development of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
The Risks of High Cholesterol for Brain Health
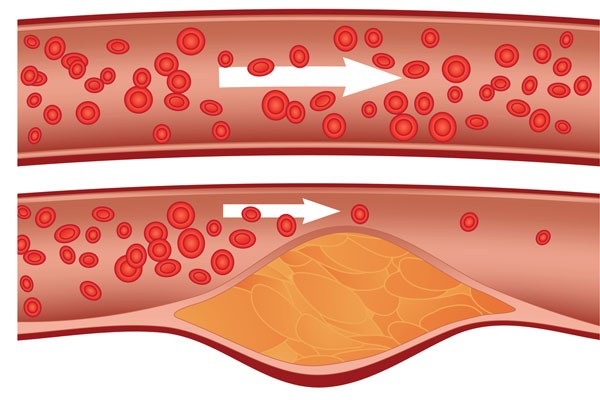
While cholesterol is essential for brain health, high levels of LDL cholesterol can be harmful. When LDL cholesterol builds up in the walls of arteries, it can lead to atherosclerosis, which is the narrowing and hardening of arteries.
Atherosclerosis can reduce blood flow to the brain and increase the risk of stroke. In addition, high levels of LDL cholesterol have been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Cholesterol plays a vital role in brain health and function. It is involved in the formation and function of synapses, the production of myelin, and the regulation of neurotransmitters. Maintaining healthy levels of cholesterol may have a number of benefits for brain health, including improved memory and cognitive function, and protection against depression, anxiety, and dementia.
However, high levels of LDL cholesterol can be harmful and increase the risk of atherosclerosis, stroke, and cognitive decline. It is important to maintain a healthy balance of cholesterol through diet and exercise, and to work with a healthcare provider to manage cholesterol levels.